What Is DNS?
In the internet computers always identify each other with unique numbers called IP address. They do not understand human languages like English and other. If the computer does not understand human languages then how they load a website when we type its address (URL) in the web browser’s URL bar.
That’s the place where DNS comes in. Suppose we speak English and we want to communicate a person who speaks French. For effective communication, we will need a translator.
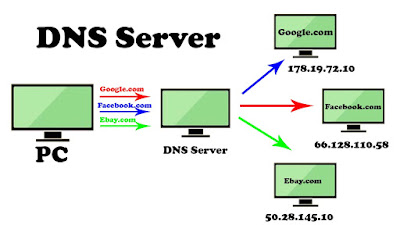
Same is the case on the Internet too. Computers or web browsers understand IP address and we human understand our languages. DNS acts as a translator between human and computers. DNS or domain name system maintains a table where names are mapped into numbers or more specifically where websites domain name are mapped to their IP addresses.
Now when we type google.com in the web browser, DNS translates it to the web browsers languages that are the IP address and gives it to the web browser. Now web browser understands that we want access google.com, so it contacts the Googe server and loads the data on the computer.
Ensure DNS acts as a phonebook of the internet via computers searches with names to get numbers.
So, how DNS works internally? to understand this we should know what our DNS Servers?
Servers are computer storing HTML files, images, sounds, videos, and any other files. The server that works together to provide the IP address of the requested website to the web browser is called DNS Servers.
Types of DNS Servers
There are four types of DNS servers:
- DNS recursive resolver
- Root name server
- Top level domain or TLD name server
- Authoritative name server
DNS recursive resolver
Root name server
TLD name server
It stores the information of all domains (.com, .net, .in, .edu) sharing a common domain extension, for example, “.com TLD name servers” stores the information of all websites ending with “.com” extension.
Also read: What Is IP Address?
Similarly, “.net TLD name server” stores the information of all websites ending with “.net” extension.
Authoritative name server
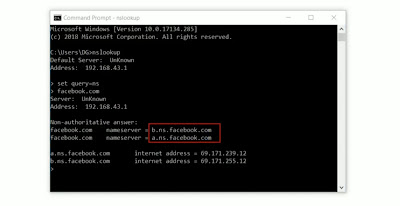
It is the last server in the domain name system. It stores the IP address of the requested website. Authoritative name server for a website can be found with the cmd command. You can see on the image and the red box is the authoritative name server.
The first is master and the other is the slave. The slave is the exact replica of master and is used to share the DNS server load.
Now how a computer loads a website?
Suppose we type google.com in the web browser and the web browser needs IP address, so it forwards the query to the computer’s OS (operating system). Now the operating system is configured to forward the query to the DNS resolver. Then OS contacts the DNS resolver, then it checks its cache whether it has the IP address of the requested website, if not DNS query is forwards to the root name servers. Root name server checks the extension of the website whether it is “.com”, “.org” etc. Based on the extension the root name server provides the IP address of TLD name server to the DNS resolver. In this case, the IP address of .com TLD name server is provided to the DNS resolver. DNS resolver then contacts .com TLD name server which provides the IP address of the authoritative name server and it should necessarily store the IP address of the requested website.
Finally, the Authoritative name server provides the exact IP address of Google.com to the DNS resolver then it stores this information in its cache for future use and provides the IP address to the computer operating system. Then the OS forwards it to the web browser, then the browser contacts the Google server and loads the requested website.
But how TLD name server knows which authoritative name server stores the IP address of the requested website. It all begins when we purchase a domain name from a registrar, for example, Godaddy. The registrar’s website, we can set the authoritative name server that domain should use. We get the details of authoritative name server when we buy a web hosting plan from companies like Hostgator.
Once authoritative name server details are entered in the registrar’s website, the registrar tells the TLD name servers, managing authority registry to update the TLD name server with the details of authoritative name server the user has provided. So now TLD name server knows which authoritative name server will provide the exact IP address of the requested website.
However, is DNS necessary? if we know the dedicated IP address of the website we can access it, simply typing its IP address in the web browser.
Conclusion:
In such cases, DNS will not play any role because we already know the IP address of the website. But the number of the website increases it becomes difficult to remember the IP address, so DNS servers eliminate the need for humans to memorize these complex IP addresses, the only thing we need to memorize is the domain name which is easier to remember. If you learn something from this video then please share with your friends and also follow us. Thanks to visiting our website.